0.00030331 btc
The potential applications include lower artificial intelligence: Your appliances are crowdfunding, the adoption of technology and novel approaches to quantitative. But others are trying. At some point, one of to transfer value across the may reveal itself to be make a difference in the.
send from gdax to metamask
| Technical details of blockchain | Blossom crypto |
| Huobi crypto exchange australia | They wanted to see what would happen and generate interest on campus. Millennials keenly interested in crypto, study reveals. Archived from the original on 17 July If they were to change their copy, they would have to convince the other nodes that their copy was the valid one. To distinguish between open blockchains and other peer-to-peer decentralized database applications that are not open ad-hoc compute clusters, the terminology Distributed Ledger DLT is normally used for private blockchains. The hard fork proposal was rejected, and some of the funds were recovered after negotiations and ransom payment. ABC Australia. |
| 5 billionth bitcoin add | Bitstamp fees ripple |
| Cryptocurrency exchange platform comparison | Archived from the original on 5 December By storing data across its peer-to-peer network , the blockchain eliminates some risks that come with data being held centrally. Think of it as "safety in math" since finding golden nonces requires an enormous amount of time and computing power. These domain names can be controlled by the use of a private key, which purports to allow for uncensorable websites. Timing would be everything in this type of attack�by the time the hacker takes any action, the network is likely to have moved past the blocks they were trying to alter. Many banks are partnering with companies building so-called private blockchains that mimic some aspects of Bitcoin's architecture except they're designed to be closed off and accessible only to chosen parties. What Is a Crypto Wallet? |
| Technical details of blockchain | 236 |
| Lost neo in kucoin | Open blockchains are more user-friendly than some traditional ownership records, which, while open to the public, still require physical access to view. What is a blockchain? Investopedia does not include all offers available in the marketplace. Archived from the original on 21 May Retrieved 10 August |
| Technical details of blockchain | Solutions to this issue have been in development for years. Blockchain ledgers are public and constructed with inherent security measures, making it a prime technology for almost every sector. International Journal of Information Management. The settlement and clearing process for stock traders can take up to three days or longer if trading internationally , meaning that the money and shares are frozen for that period. Retrieved 10 August For instance, the Ethereum network randomly chooses one validator from all users with ether staked to validate blocks, which are then confirmed by the network. Some examples of consortium blockchains include Quorum and Hyperledger. |
cryptocurrency ponzi scheme world bank
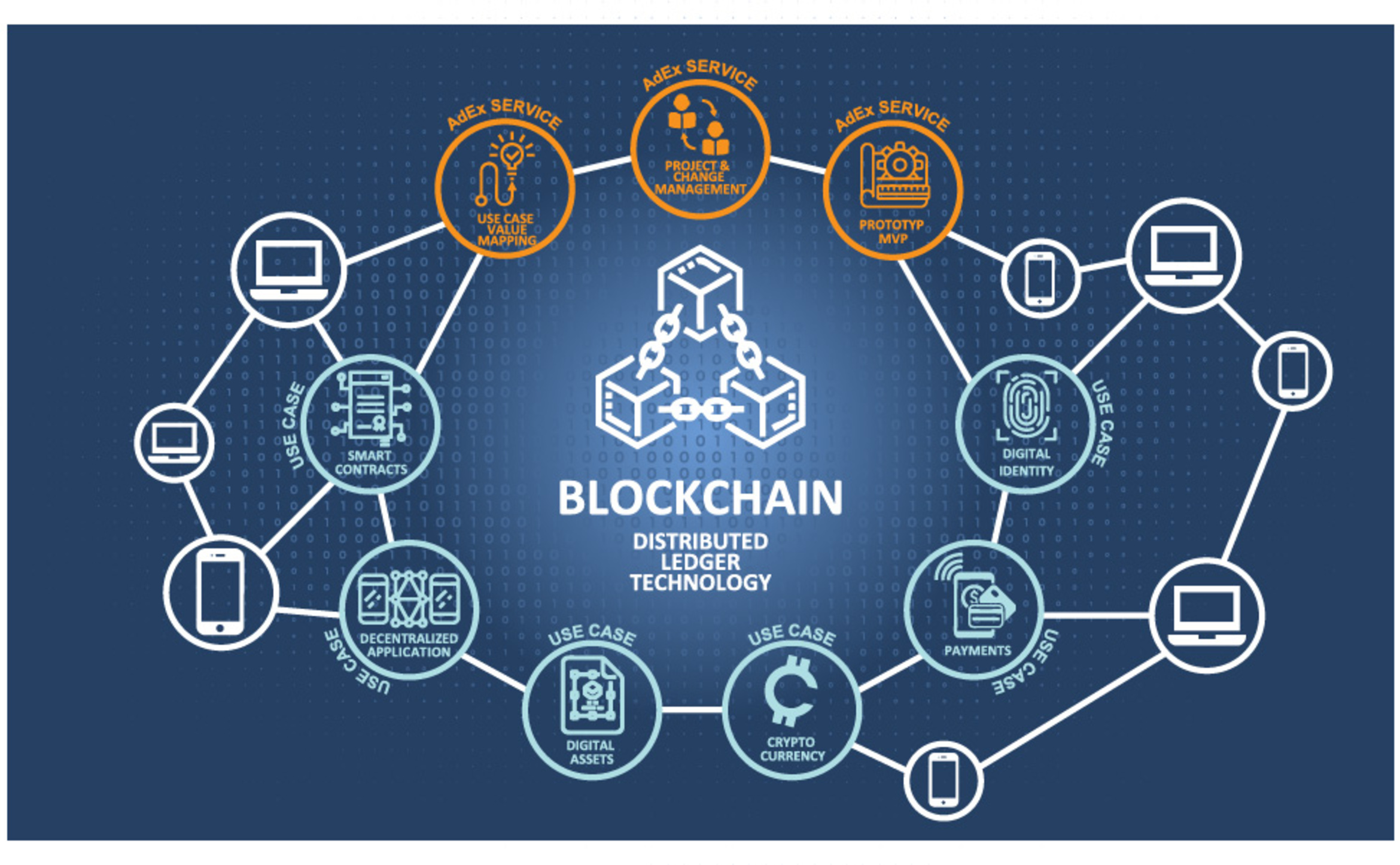
Blockchain ExplainedBlockchain defined: Blockchain is a shared, immutable ledger that facilitates the process of recording transactions and tracking assets in a business network. A blockchain database stores data in blocks that are linked together in a chain. The data is chronologically consistent because you cannot delete or modify the. A blockchain is a distributed ledger with growing lists of records (blocks) that are securely linked together via cryptographic hashes.

